Jie Liu
Associate Professor
University of Michigan
Liu Lab
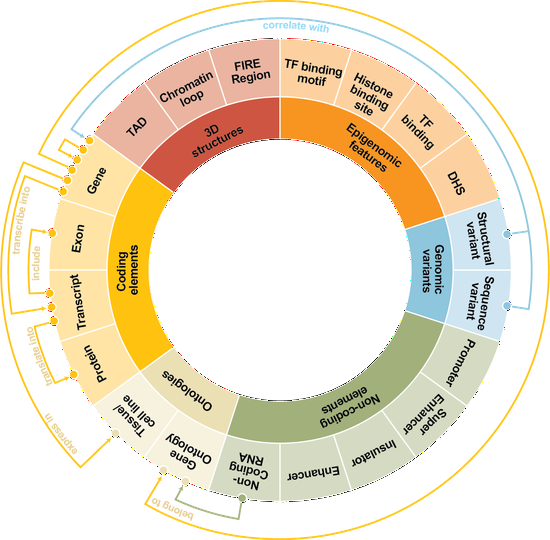
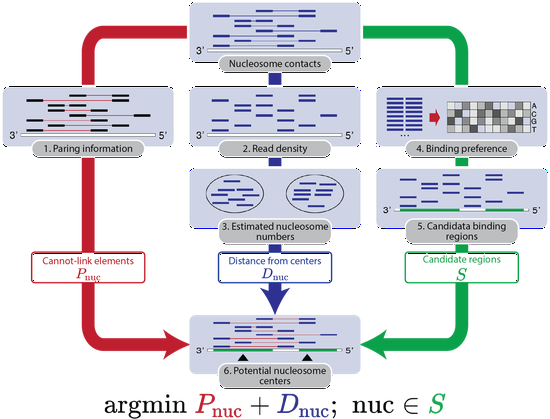
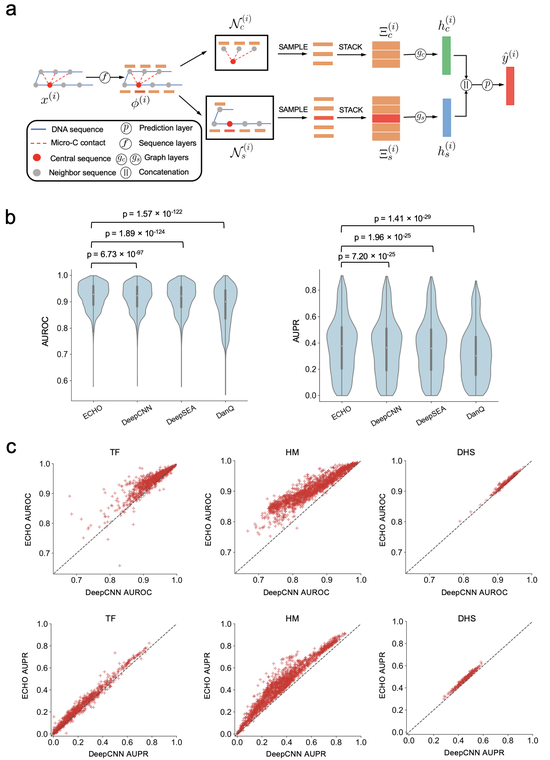
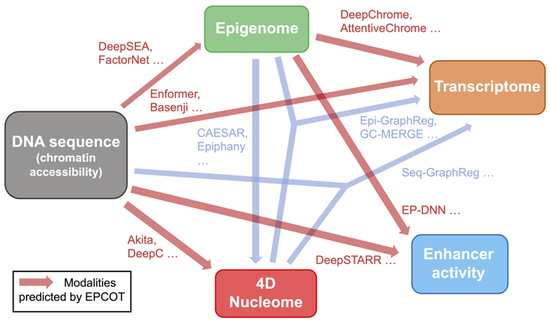
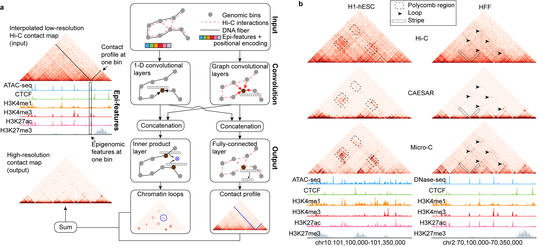
Dr. Liu’s research lab develops computational methods, tools, and resources for understanding the human genome and diseases such as diabetes. Recently, the methodology focuses are knowledge graphs and foundation models. We have developed a knowledge graph GenomicKB to accumulate human-readable knowledge about the human genome. We have extracted genomic knowledge from PubMed and developed another knowledge graph GLKB. We have also developed a genomic foundation model EPCOT which comprehensively predicts multiple genomic modalities.
The lab currently participates in several NIH consortia, including 4DN, IGVF, HIRN, CFDE, and the recent PanKbase program. In particular, Dr. Liu co-leads the Machine Learning Focus Group at IGVF, co-leads the Data/Metadata Working Group at PanKbase, and leads the development of PanKgraph, the knowledge graph within the PanKbase system.
Interests
- Machine Learning
- Bioinformatics
- Computational Genomics
- Medical Informatics
Education
-
PhD in Computer Science, 2014
University of Wisconsin - Madison